Gammapathies monoclonales
De médecine.top
Révision datée du 6 septembre 2020 à 12:38 par Julien (discussion | contributions) (→Myélome multiple Cours Prof Vollenweider, Service de médecine interne, UNIL-CHUV 2017)
Caractéristiques communes
Neuropathies associated with monoclonal proteins occur in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance, multiple myeloma, Waldenström macroglobulinemia, amyloidosis, and other hematologic malignancies.
Bilan étiologique
| Paramètre | Question | Remarque |
|---|---|---|
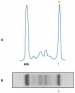
| Electrophorèse des protéines sériques/urinaires | Recherche d'une protéinémie/protéinurie monoclonale | |
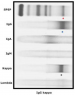
| Immunofixation des protéines sériques/urinaires | Caractérisation de la paraprotéine | Meilleure sensibilité que l'électrophorèse pour chaînes légères en particulier → recherche de la protéine de Bence-Jones dans les urines pour le myélome multiple |
| Dosage des chaînes légères libres sériques | Recherche d'un rapport kappa/lambda anormal | Si absence de gammapathie monoclonale, rapport kappa/lambda ≈ 1 |
| Protéine de Bence-Jones dans les urines | Recherche d'une gammapathie monoclonale à chaîne légère | CAVE le stix urinaire ne réagit qu'avec l'albumine et pas aux chaînes légères dans les urines |
| Ponction-biopsie de moelle osseuse | Recherche d'une plasmocytose médullaire monoclonale |
MGUS
Monoclonal Gammopathy of Undetermined Significance
- Caractéristiques:
- Paraprotéine sérique < 30 g/l et
- Plasmocytose médullaire clonale < 10%
- Pas d’atteinte d’organe/tissus en relation (CRAB) et pas d’amyloïdose
- Complications et progression:
- IgM MGUS has the potential to progress to Waldenström macroglobulinemia at a rate of 1.5% per year
- Light-chain MGUS can progress to other PCDs at a rate of 0.3%
- In addition to the risk of progression, patients with MGUS are at higher risk of osteoporosis and fracture of the axial skeleton
- Suivi:
- Bone mineral density testing should be considered. Treatment is not required at diagnosis.
- Si paraprotéinémie 15 g/l et dosage des chaînes légères normal et électrophorèse des protéines urinaires normale, le risque de progression est bas. Pas d'évaluation extensive nécessaire
- Patients commonly undergo follow-up for signs and symptoms of progression, initially at 6 months and then yearly, if stable.
Myélome asymptomatique
- Caractéristiques:
- Paraprotéine sérique (IgG ou IgA) > 30 g/L ou immunoglobulinurie > 500 mg/24h et
- Plasmocytose médullaire clonale entre 10 et 60%
- Pas d’atteinte d’organe/tissus en relation
- Suivi
- All patients with MM should be assessed for skeletal lesions at diagnosis, periodically thereafter, and when any new symptoms occur.
- The International Myeloma Working Group recommends that all patients with smoldering multiple myeloma undergo whole body MRI to assess for lytic lesions.
Hémopathies malignes
Myélome multiple [1]
- Paraprotéinémie à IgG
- Rechercher une paraprotéinémie monoclonale
- Doser chaines légères libres dans le plasma
- Si nécessaire chaines légères dans urine de 24 heures
- Rechercher des attentes d’organe: CRAB
- Calcium >2,8 mmol/l (ou >0,3 mmol/l de plus que la limite haute)
- Créatinine >177 mcmol/l ou eGFR <40 ml/min
- Hémoglobine <100 g/l ou 20 g/l en-dessous de la limite basse
- Rx standards ≥ 1 lésion lytique
- Ponction biopsie de moelle osseuse
- Other possible symptoms include fatigue, weight loss, neuropathy, and those arising from extramedullary plasmacytoma.
- Pronostic: dosage de la β2-microglobuline
- Traitement:
- Greffe autologue de cellules souches hématopoïétiques: non curative mais amélioration de la survie sans progression et de la survie totale
- Biphosphonates: Zoledronic acid has also been shown to improve survival in MM requiring therapy
- Si rechute/maladie réfractaire: Several new drugs have been approved in this setting, including proteasome inhibitors (carfilzomib and ixazomib), the immunomodulatory drug pomalidomide (Imnovid), histone deacetylase inhibitors (panobinostat), and monoclonal antibodies (daratumumab and elotuzumab).
Plasmocytome isolé
Maladie de Waldenström
Syndrome lymphoprolifératif à IgM. Synonyme: lymphome lymphoplasmocytaire
- Caractéristiques:
- Paraprotéine sérique (IgM) > 30 g/l
- Plasmocytose médullaire clonale > 10%
- Atteinte d'organes cibles
- Diagnostic: ponction-biopsie de moelle osseuse
- Traitement:
- Symptomatic hyperviscosity requires emergent treatment with plasmapheresis to remove excess IgM.
- Therapy to decrease IgM production is instituted simultaneously in patients with hyperviscosity symptoms and should be initiated in other patients with symptomatic WM. Rituximab, either as a single agent or in combination with chemotherapy such as cyclophosphamide, bendamustine, and bortezomib, along with glucocorticoids, is commonly used. Recently, ibrutinib (a Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor) has been approved for treatment of WM.
- As in multiple myeloma, patients with smoldering, asymptomatic WM can be observed without therapy.
Leucémie lymphoïde chronique
Amyloïdose
- Souvent lambda
Maladie des chaînes lourdes
POEMS
Polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, monoclonal gammopathy, and skin changes
- Paraprotéinémie souvent à IgG/IgA et lambda
- POEMS syndrome is characterized by the presence of a monoclonal plasma cell disorder, peripheral neuropathy, and one or more of the following: osteosclerotic myeloma, Castleman disease (angiofollicular lymph node hyperplasia), elevated serum vascular endothelial growth factor, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, edema, typical skin changes, and papilledema.
Références
- ↑ Cours Prof Vollenweider, Service de médecine interne, UNIL-CHUV 2017