Différences entre versions de « Hépatites virales »
De médecine.top
| Ligne 33 : | Ligne 33 : | ||
Exceptions: patients >40 ans, virémie >1 mio ET inflammation et fibrose | Exceptions: patients >40 ans, virémie >1 mio ET inflammation et fibrose | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | '''Phase immunoréactive'''<br>HBeAg pos ou HBeAg nég |
| + | | + | ||
| - | | - | ||
Version du 18 avril 2020 à 14:04
Hépatite B
Infection chronique à HBV
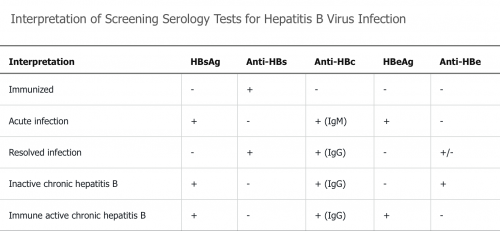
| HBsAg | anti-HBs | anti-HBc | HBeAg | anti-HBe | HBV DNA | ALAT | Prise en charge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interprétation | Infection aiguë ou chronique | Infection résolue ou vaccination | Infection actuelle ou passée | Réplication active | Infection inactive ou mutant | |||
| Phase immunotolérante Âge < 30 ans |
+ | + | - | > 1 million | Normal | Absence d'inflammation hépatique.
Suivi ALAT +/- alpha-FP/US. Exceptions: patients >40 ans, virémie >1 mio ET inflammation et fibrose | ||
| Phase immunoréactive HBeAg pos ou HBeAg nég |
+ | - | + (IgG) OK ??? | + | - (?) | > 20 000 IU/ml | ↑ | Inflammation et fibrose
Traitement nécessaire. |
| + | - | + (IgG) OK ??? | - | - (?) | > 2000 IU/ml | |||
| Hépatite B chronique inactive = porteur inactif |
+ | - | + (IgG) OK ??? | - | + | < 2000 IU/ml | Normal | Pas d'inflammation, fibrose variable
Suivi de l'HBV DNA 3-4x/an |
| Hépatite B résolue | - | + | + (IgG) | - | +/- | - | Normal | CAVE si immunosupression |
| Réactivation | + (perte de contrôle immun) | + | ↑ de la virémie de base | ↑ à 3x >100 U/l |