Différences entre versions de « Hépatites virales »
De médecine.top
| Ligne 82 : | Ligne 82 : | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | + | === Complications === | |
| + | The following characteristics are associated with an increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with HBV infection and are indications for surveillance with ultrasound or cross-sectional imaging every 6 months: | ||
| + | # cirrhosis; | ||
| + | # Asian descent plus male sex plus age older than 40 years; | ||
| + | # Asian descent plus female sex plus age older than 50 years; | ||
| + | # sub-Saharan African descent plus age older than 20 years; | ||
| + | # persistent inflammatory activity (defined as an elevated ALT level and HBV DNA levels greater than 10,000 IU/mL for at least a few years); | ||
| + | # a family history of hepatocellular carcinoma.<ref>https://mksap18.acponline.org/app/topics/gi/mk18_a_gi_s6/mk18_a_gi_s6_2_2</ref> | ||
| + | == Références == | ||
[[Category:Gastro-entérologie]] | [[Category:Gastro-entérologie]] | ||
[[Category:Infectiologie]] | [[Category:Infectiologie]] | ||
Version du 18 avril 2020 à 14:58
Hépatite B
Infection chronique à HBV
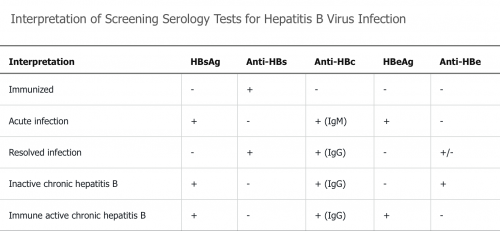
| HBsAg | anti-HBs | anti-HBc | HBeAg | anti-HBe | HBV DNA | ALAT | Prise en charge | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Interprétation | Infection aiguë ou chronique | Infection résolue ou vaccination | Infection actuelle ou passée | Réplication active | Infection inactive ou mutant | |||
| Phase immunotolérante Âge < 30 ans |
+ | + | - | > 1 million | Normal | Absence d'inflammation hépatique.
Suivi ALAT +/- alpha-FP/US. Exceptions: patients >40 ans, virémie >1 mio ET inflammation et fibrose | ||
| Phase immunoréactive HBeAg pos ou HBeAg nég |
+ | - | + (IgG) OK ??? | + | - (?) | > 20 000 IU/ml | ↑ | Inflammation et fibrose
Traitement nécessaire. |
| + | - | + (IgG) OK ??? | - | - (?) | > 2000 IU/ml | |||
| Hépatite B chronique inactive = porteur inactif |
+ | - | + (IgG) OK ??? | - | + | < 2000 IU/ml | Normal | Pas d'inflammation, fibrose variable
Suivi de l'HBV DNA 3-4x/an |
| Hépatite B résolue | - | + | + (IgG) | - | +/- | - | Normal | CAVE si immunosupression |
| Réactivation | + (perte de contrôle immun) | + | ↑ de la virémie de base | ↑ à 3x >100 U/l |
Complications
The following characteristics are associated with an increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with HBV infection and are indications for surveillance with ultrasound or cross-sectional imaging every 6 months:
- cirrhosis;
- Asian descent plus male sex plus age older than 40 years;
- Asian descent plus female sex plus age older than 50 years;
- sub-Saharan African descent plus age older than 20 years;
- persistent inflammatory activity (defined as an elevated ALT level and HBV DNA levels greater than 10,000 IU/mL for at least a few years);
- a family history of hepatocellular carcinoma.[1]