Insuffisance rénale chronique
De médecine.top
Définition (KDIGO 2012)
La maladie rénale chronique est définie par:
- des anomalies de la structure ou fonction rénale (protéinurie, albuminurie, hématurie, leucocyturie),
- présentes depuis >3 mois,
avec impact sur la santé, dont la classification est basée sur la cause, le (e)GFR et l'albuminurie (cf ci-dessous).[1]
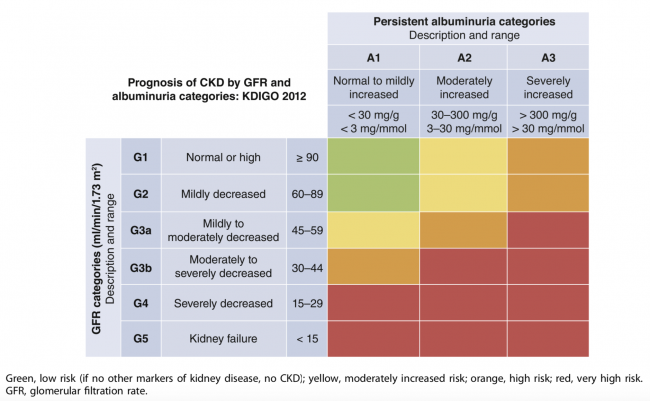
Stades
- Rapport albumine/créatinine g/mol = mg/mmol
- Estimation de la GFR:
- Tableau ici
- Cockroft-Gault: +) -) importance du poids (extrêmes peuvent fausser les valeurs)
- MDRD: meilleure pour les DFG < 60 ml/min/1.73m2
- Facteurs prédictifs de progression vers l'insuffisance rénale terminale (KDIGO 2012):
- Niveau basal de l'eGFR
- Degré de protéinurie/albuminurie
Bilan
- Spot: créatinine, albumine, protéines
- Echographie des voies urinaires: exclusion d'une cause post-rénale
Prise en charge
Tension artérielle
- IEC/ARB si stade KDIGO G3a ou au-delà ou si stade G1/G2 avec albuminurie, diurétiques de l'anse
- Cible: <130/80 mmHg
Lipides
The Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes guidelines recommend treatment with a statin
- in all patients with non-dialysis–dependent chronic kidney disease (CKD) who are over 50 years of age
- and in adults 18 to 49 years of age with non-dialysis–dependent CKD and any one of the following: coronary disease, diabetes mellitus, prior ischemic stroke, or a >10% estimated risk of coronary death or nonfatal myocardial infarction.
- Cible en présence de diabète de type 2:
- LDL cholestérol <1,8 mmol/l si absence d'albuminurie
- LDL cholestérol <1,4 mmol/l si présence d'albuminurie
Calcium, phosphate et vitamine D
- Vitamine D
- Effets: ↑ Ca2+
- KDIGO guidelines recommend that patients with an eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 (stage G3-G5) be evaluated for 25-hydroxyvitamin D deficiency and supplemented as per guidelines for the general population.
- Phosphate
- Current KDIGO guidelines recommend that in patients with CKD stages G3a to G5, elevated phosphorus levels should be lowered toward the normal range → Sevelamercarbonate
- Calcium
- KDIGO guidelines recommend avoiding hypercalcemia. Mild and asymptomatic hypocalcemia (for example, in the context of calcimimetic treatment) can be tolerated to avoid inappropriate calcium loading.
- PTH
- Effets: ↑ Ca2+, ↓ Ph−
- The 2016 KDIGO update suggests that patients with levels of intact PTH “progressively rising or persistently above the upper normal limit for the assay be evaluated for modifiable factors, including hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, high phosphate intake, and vitamin D deficiency.” KDIGO guidelines recommend against routine use of calcitriol and vitamin D analogues to lower PTH levels in patients with CKD stages G3a to G5 not on dialysis, because trials of these agents failed to demonstrate improvements in clinically relevant outcomes. Instead, these agents should be reserved for patients with CKD stages G4 to G5 with severe and progressive hyperparathyroidism.
- In patients on dialysis, KDIGO guidelines recommend use of calcimimetics, calcitriol, or vitamin D analogues, or a combination of calcimimetics and calcitriol or vitamin D analogues, to lower PTH levels.
- Voir aussi: hyperparathyroïdie secondaire
Hémoglobine et fer
- Fer
- Coefficient de saturation de la transferrine cible: > 30%
- Ferritine cible: > 500 μg/l
- Hémoglobine
- Hb cible: 110 g/l
- Erythropoïétine (EPO) si Hb < 100 g/l
- Minimiser les transfusions sanguines → risque d'allo-immunisation
- Epargne du capital veineux du membre supérieur → en cas de confection future d'une fistule de dialyse
- Hb cible: 110 g/l
Désordres acido-basiques
- Bicarbonates
- (KDIGO) guidelines recommend treatment of metabolic acidosis with alkali therapy in patients with chronic kidney disease when the serum bicarbonate is chronically <22 mmol/l → Nephrotrans®
- The alkali salt therapy dose should be titrated to achieve a serum bicarbonate level within the normal range
Complications
- Hyperparathyroïdisme secondaire (cf ci-dessus)
Désordres du métabolisme minéral et osseux
Ostéopathies à bas niveau de remodelage
- Os adynamique
- Ostéomalacie
Ostéopathies à haut niveau de remodelage
- Ostéite fibreuse