Différences entre versions de « Lymphomes »
De médecine.top
| Ligne 37 : | Ligne 37 : | ||
==== Lymphome de Burkitt ==== | ==== Lymphome de Burkitt ==== | ||
Prophylaxis to manage tumor lysis syndrome should be instituted before initiation of chemotherapy for patients with Burkitt lymphoma. | Prophylaxis to manage tumor lysis syndrome should be instituted before initiation of chemotherapy for patients with Burkitt lymphoma. | ||
| + | * Association avec EBV | ||
==== Lymphomes B folliculaires ==== | ==== Lymphomes B folliculaires ==== | ||
| Ligne 44 : | Ligne 45 : | ||
==== Lymphomes T périphériques NOS (not otherwise specified) ==== | ==== Lymphomes T périphériques NOS (not otherwise specified) ==== | ||
==== Lymphomes T angioimmunoblastiques (AILT) ==== | ==== Lymphomes T angioimmunoblastiques (AILT) ==== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Lymphome de Hodgkin == | == Lymphome de Hodgkin == | ||
Version du 30 mai 2020 à 15:37
Caractéristiques
- Clinique: lymphadénopathie
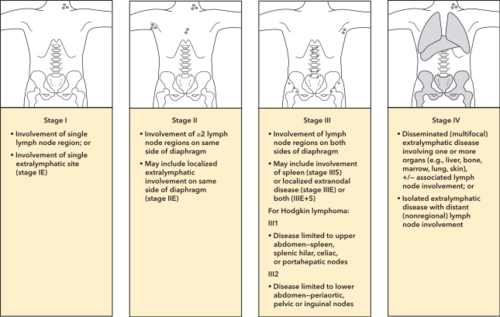
Staging
Classification de Ann Arbor
Lymphomes non-hodgkiniens
Lymphomes à cellules B
80-85% des lymphomes sont des lymphomes malins non-Hodgkiniens avec une large majorité de lymphomes B
Lymphome B à grandes cellule (DLBCL)
- Caractéristiques: Lymphome aggressif. 3 sous-types: lymphome « germinal center like », lymphome « Activate B cell », lymphome primaire du médiastin
- Clinique: Se présente avec une masse tumorale de croissance rapide
- Pronostic: basé sur score IPI[1] (5 paramètres)
- Age > 60 ans
- Stade III-IV
- Score performance ECOG (0-1 vs 2-4)
- LDH (>N)
- Sites extraganglionnaires (>1)
- Lymphomes à haut risque:
- IPI élevé
- Présence de deux réarrangements (“double hit”) en particulier BCL-2 t(14;18) et MYC t(8;14)
- (Phénotype non germinal center)
- Traitement: Objectif curatif R-CHOP
- Si récidive: In addition to further standard chemotherapy, autologous HSCT and anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy may be used as salvage therapy in patients who relapse.
Lymphome du manteau
- Caractéristiques: Cellules lymphoïdes B issues cellules B "naïves" du manteau folliculaire
- Génétique: Associé à la translocation t(11;14) → surexpression de la cycline D1
- Clinique: adénopathies, splénomégalie, atteinte muqueuse digestive
- Pronostic:
- Traitement: Objectif non curatif alternance R-CHOP et R-DHAP suivi d'une autogreffe
- Si récidive/réfractaire: Ibrutinib (anti-BTK)
Lymphome de Burkitt
Prophylaxis to manage tumor lysis syndrome should be instituted before initiation of chemotherapy for patients with Burkitt lymphoma.
- Association avec EBV
Lymphomes B folliculaires
Lymphomes à cellules T et à cellules NK
10-12% sont des lymphomes T ou NK
Lymphomes T périphériques NOS (not otherwise specified)
Lymphomes T angioimmunoblastiques (AILT)
Lymphome de Hodgkin
A negative PET scan may obviate the need for bone marrow biopsies in many patients with Hodgkin and large cell lymphoma, but PET scans are not sensitive to very indolent lymphomas.
- ↑ NEJM 1993; vol 329