Lymphomes
De médecine.top
Révision datée du 1 juin 2020 à 17:10 par Julien (discussion | contributions) (→Lymphome B folliculaires)
Caractéristiques
- Clinique: lymphadénopathie
Staging
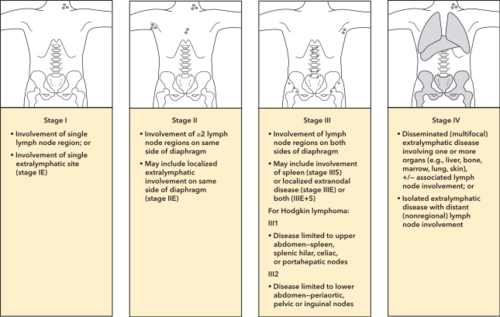
Classification de Ann Arbor
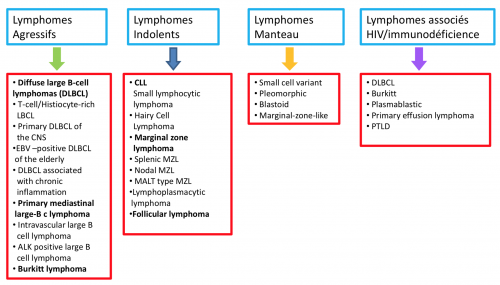
Lymphomes non-hodgkiniens
Lymphomes à cellules B
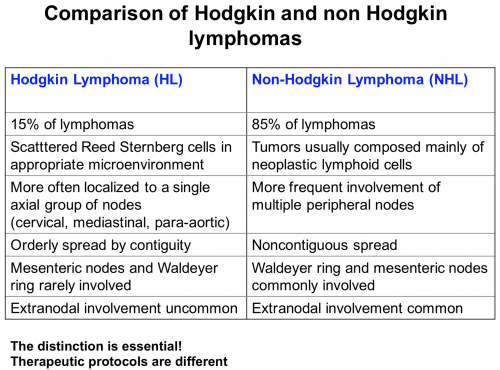
80-85% des lymphomes sont des lymphomes malins non-Hodgkiniens avec une large majorité de lymphomes B
Lymphome B à grandes cellule (DLBCL)
- Caractéristiques: Lymphome aggressif. 3 sous-types: lymphome « germinal center like », lymphome « Activate B cell », lymphome primaire du médiastin
- Clinique: Se présente avec une masse tumorale de croissance rapide
- Pronostic: basé sur score IPI[1] (5 paramètres)
- Age > 60 ans
- Stade III-IV
- Score performance ECOG (0-1 vs 2-4)
- LDH (>N)
- Sites extraganglionnaires (>1)
- Lymphomes à haut risque:
- IPI élevé
- Présence de deux réarrangements (“double hit”) en particulier BCL-2 t(14;18) et MYC t(8;14)
- (Phénotype non germinal center)
- Traitement: Objectif curatif R-CHOP
- Si récidive: In addition to further standard chemotherapy, autologous HSCT and anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy may be used as salvage therapy in patients who relapse.
Lymphome du manteau
- Caractéristiques: Cellules lymphoïdes B issues cellules B "naïves" du manteau folliculaire
- Génétique: translocation t(11;14) → surexpression de la cycline D1
- Clinique: adénopathies, splénomégalie, atteinte muqueuse digestive
- Pronostic:
- Traitement: Objectif non curatif alternance R-CHOP et R-DHAP suivi d'une autogreffe
- Si récidive/réfractaire: Ibrutinib (anti-BTK)
Lymphome de Burkitt
- Caractéristiques: Lymphome très aggressif. Association avec EBV (forme endémique ou associée à une immunodéficience) ou forme sporadique.
- Génétique: translocation t(8;14) → surexpression MYC
- Traitement: Objectif curatif avec guérison ~70 %
- Prophylaxis to manage tumor lysis syndrome should be instituted before initiation of chemotherapy for patients with Burkitt lymphoma: the most appropriate treatment is the administration of rasburicase along with intravenous hydration with normal saline and furosemide.
Lymphome B folliculaires
- Caractéristiques: Lymphome indolent. Progressions-rechutes toujours plus rapprochées sur une longue période. Follicular lymphomas are classified based on their dominant cell type: predominantly smaller cells (grade 1), a mixture of smaller and larger cells (grade 2), and predominantly large cells (grade 3).
- Génétique: translocation t(14;18) → surexpression de l'oncogène BCL2
- Pronostic: survie médiane ≥ 10 ans, risque de transformation en lymphome agressif → biopsie en cas de rechute ou transformation en lymphome diffus à grandes cellules B
- Score pronostique FLIPI 2
- Traitement: Objectif non curatif Traitement d'induction suivi d'un traitement de maintenance par Rituximab
- Transformation en lymphome agressif: chimiothérapie de type R-CHOP (prise en charge comme un lymphome agressif)
Leucémie lymphoblastique chronique (LLC)
- Voir aussi la page Leucémies
Small lymphocytic lymphoma
CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma represent the same disease, with the designation as leukemia or lymphoma based on the dominant clinical manifestation in either peripheral blood and marrow or nodal involvement, respectively. Both CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma are treated the same.
Lymphomes à cellules T et à cellules NK
10-12% sont des lymphomes T ou NK
Lymphomes T périphériques NOS (not otherwise specified)
Lymphomes T angioimmunoblastiques (AILT)
Lymphome de Hodgkin
A negative PET scan may obviate the need for bone marrow biopsies in many patients with Hodgkin and large cell lymphoma, but PET scans are not sensitive to very indolent lymphomas.
Références
- ↑ NEJM 1993; vol 329