Différences entre versions de « Dyslipidémie »
De médecine.top
| (8 versions intermédiaires par le même utilisateur non affichées) | |||
| Ligne 25 : | Ligne 25 : | ||
** Adults of '''any age''' with an LDL cholesterol level of 4.92 mmol/L or higher should be started on high-intensity statin therapy<ref>American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology cholesterol treatment guideline</ref> | ** Adults of '''any age''' with an LDL cholesterol level of 4.92 mmol/L or higher should be started on high-intensity statin therapy<ref>American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology cholesterol treatment guideline</ref> | ||
** Adults '''aged 40 to 75 years''' with diabetes should be started on moderate-intensity statin therapy. | ** Adults '''aged 40 to 75 years''' with diabetes should be started on moderate-intensity statin therapy. | ||
| − | ** In adults aged '''40 to 75 years''' who have at least one ASCVD risk factor (dyslipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, or smoking) and a calculated 10-year ASCVD risk of 10% or greater | + | ** In adults aged '''40 to 75 years''' who have: |
| + | *** at least one ASCVD risk factor (dyslipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, or smoking) '''<u>and</u>''' | ||
| + | *** a calculated 10-year ASCVD risk of 10% or greater | ||
| + | :: the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends statin therapy for the primary prevention of ASCVD. | ||
* <u>Avec calcul du score de risque au préalable:</u> | * <u>Avec calcul du score de risque au préalable:</u> | ||
| − | ** Patients with a 10-year risk for ASCVD of 20% or higher. | + | ** Patients with a '''10-year risk for ASCVD of 20% or higher'''. |
=== Prévention secondaire === | === Prévention secondaire === | ||
| − | Chez les patients suivants (= atteints d'ASCVD): | + | * <u>Chez les patients suivants (= atteints d'ASCVD):</u> |
| − | * [[Syndrome coronarien aigu]] | + | ** [[Syndrome coronarien aigu]] |
| − | * Antécédent d'infarctus du myocarde | + | ** Antécédent d'infarctus du myocarde |
| − | * [[Angor stable]] et instable | + | ** [[Angor stable]] et instable |
| − | * Antécédent de revascularisation artérielle (coronarienne ou autre) | + | ** Antécédent de revascularisation artérielle (coronarienne ou autre) |
| − | * Antécédent d'[[Stroke unit|AVC ou AIT]] | + | ** Antécédent d'[[Stroke unit|AVC ou AIT]] |
| − | * AOMI attribuable à l'athérosclérose (ABI ≤ 0,9) | + | ** AOMI attribuable à l'athérosclérose (ABI ≤ 0,9) |
| − | * [[Anévrisme aortique]] | + | ** [[Anévrisme aortique]] |
| − | + | : → High-intensity statin therapy should be initiated in patients with ASCVD who are aged ≤ 75 years to achieve a reduction in LDL cholesterol of 50% or greater. | |
| − | + | : → If high-intensity statin therapy is contraindicated or not tolerated, moderate-intensity statin therapy should be initiated to achieve a reduction in LDL cholesterol of 30% to 49%. | |
=== Laboratoire === | === Laboratoire === | ||
Version actuelle datée du 14 octobre 2021 à 15:51
Dépistage
- Recommandé chez tous les adultes entre 40 et 75 ans[1]
Diagnostic différentiel
- Hypothyroïdie
- Diabète non contrôlé
- Syndrome néphrotique
- Médicaments: glucocorticoïdes, diurétiques, amiodarone
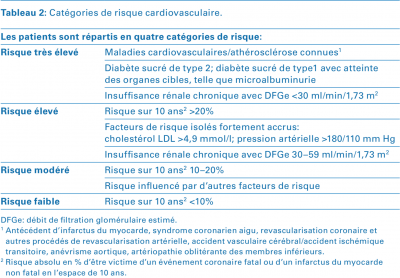
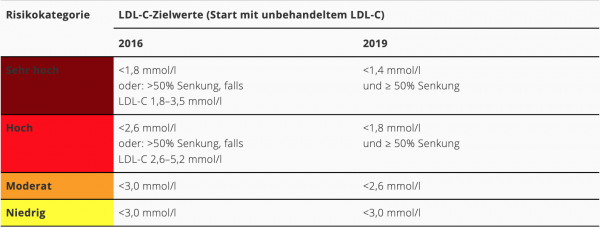
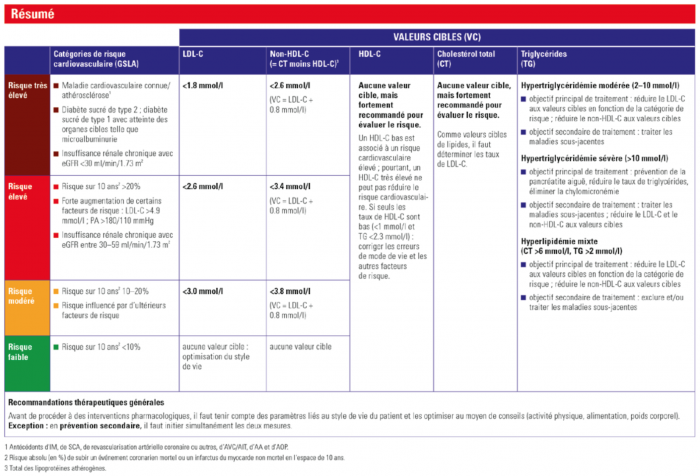
Stratification du risque cardiovasculaire (Suisse, 2018 et 2019)
- Calculateurs:
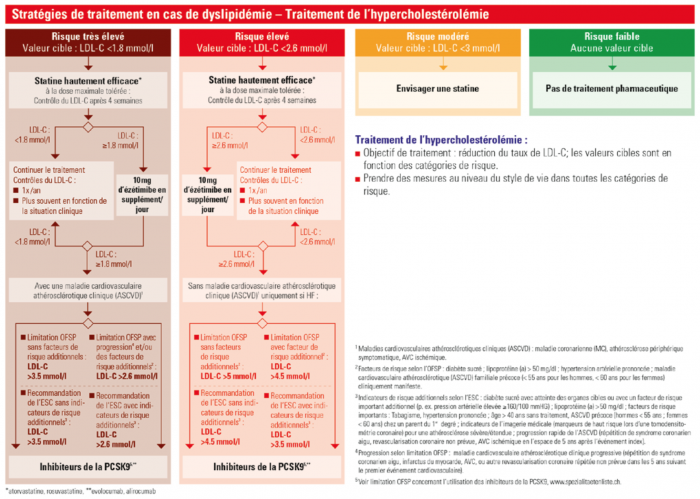
Traitement de l'hypercholestérolémie (Suisse, 2018)
Hypercholestérolémie
Prévention primaire
- Sans calcul du score de risque préalable:[2]
- Adults of any age with an LDL cholesterol level of 4.92 mmol/L or higher should be started on high-intensity statin therapy[3]
- Adults aged 40 to 75 years with diabetes should be started on moderate-intensity statin therapy.
- In adults aged 40 to 75 years who have:
- at least one ASCVD risk factor (dyslipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, or smoking) and
- a calculated 10-year ASCVD risk of 10% or greater
- the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends statin therapy for the primary prevention of ASCVD.
- Avec calcul du score de risque au préalable:
- Patients with a 10-year risk for ASCVD of 20% or higher.
Prévention secondaire
- Chez les patients suivants (= atteints d'ASCVD):
- Syndrome coronarien aigu
- Antécédent d'infarctus du myocarde
- Angor stable et instable
- Antécédent de revascularisation artérielle (coronarienne ou autre)
- Antécédent d'AVC ou AIT
- AOMI attribuable à l'athérosclérose (ABI ≤ 0,9)
- Anévrisme aortique
- → High-intensity statin therapy should be initiated in patients with ASCVD who are aged ≤ 75 years to achieve a reduction in LDL cholesterol of 50% or greater.
- → If high-intensity statin therapy is contraindicated or not tolerated, moderate-intensity statin therapy should be initiated to achieve a reduction in LDL cholesterol of 30% to 49%.
Laboratoire
- ALAT uniquement avant l'introduction d'une statine
- Tests hépatiques complets et CK seulement si symptômes ou avant d'initier le traitement chez un patient à risque (myopathie)
Suivi
- Profil lipidique 4-12 semaines après l'introduction du traitement
- Puis profil lipidique aux 3 mois/12 mois
Hypertriglycéridémie
- Xanthomes éruptifs (surface des extenseurs, fesses) -> pathognomoniques d'une hypertriglycéridémie
Références
- 2019 https://medicalforum.ch/fr/online-magazine/post/esc-kommentar-agla
- 2018 https://www.swisscardio.ch/DOCS_PUBLIC/Empfehlungen_Richtlinien/AGLA_Editorial_Neue_Empfehlungen_F.pdf
- 2018 https://www.swisscardio.ch/DOCS_PUBLIC/Empfehlungen_Richtlinien/AGLA_Neue_Empfehlungen_F.pdf
- ↑ The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) recommends universal lipid screening in adults aged 40 to 75 years to calculate risk for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) using the American Heart Association (AHA)/American College of Cardiology (ACC) Pooled Cohort Equations
- ↑ https://mksap18.acponline.org/app/topics/gm/mk18_b_gm_s9/mk18_b_gm_s9_2_2
- ↑ American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology cholesterol treatment guideline